Weep 3 forms of the verb. Irregular English verbs. Verbs with -d changed to -t
Verb- this is an independent part of speech that answers the questions what to do ?, what to do? (be, learn, dream, go…)
According to the method of formation of past tense forms (V2) and past participles (V3), all English verbs are divided into 2 groups: regular (Regular Verbs) and irregular verbs (Irregular verbs).

The English verb has three forms. The verb forms are denoted by Roman numerals I, II, III.
I form(or an infinitive without to), for example: to make (to do) - make - the first, or main form that answers the question what to do ?, what to do? With the help of the first form of the verb, the Present Simple Tense is formed. When forming Present Simple Tense, the ending is added to the I form of the verb in the 3rd person singular (he, she, it - he, she, it) -s or -es(he jumpes, she jumpes, it jumpes, he cries, she cries, it cries, he does, she does, it does) . With the rest of the pronouns (I, we, you, you, they - I, we, you, you, they), the I form of the verb is used unchanged.
II form serves to form the simple past tense (Past Simple Tense). When forming the simple past tense, both regular and irregular verbs are used. Regular verbs form II and III forms by adding the suffix form I to the stem –ed(jump - jumped - jump - jumped) . If the verb is not regular, then its past tense form corresponds to the second column in the table of irregular verbs (be - was / were, do - did, make - made).
III form- Participle II (Participle II) - a special form of the verb that denotes a sign of an object by action and answers the questions of an adjective (lost, baked, done). For regular verbs III, the form coincides with II: jump (I) - jumped (II) - jumped (III) (jump - jumped - jumped). II and III forms of irregular verbs can be formed in various ways, indicated below.
Regular verbs
Regular verbs form II and III forms by adding the suffix form I to the stem – ed (- d), which is pronounced like:
- [ d] after vowels and voiced consonants: to clean (clean) - cleaned (cleaned); to play (play) - played (played);
- [ t] after the deaf: to work (work) - worked (worked), to look (watch) - looked (looked);
- after [d] And [t]: to want (want) - wanted (wanted), to mend (repair) - mended (repaired).
When forming II and III forms of verbs, pay attention to the following spelling rules:
- If the I form is a short root syllable and ends with one consonant, then when adding the ending –ed the last vowel of the root is doubled: to stop (stop) - sto pped(has stopped).
- -y, preceded by a consonant, the letter y changes to i: to carry (carry) - carried (carried), to study (learn) - studied (studied). But if the stem of the verb ends in -y, which is preceded by a vowel, then the stem of the verb is simply added - ed: to play (play) - played (played), to stay (stay) - stayed (stayed).
- If the stem of the verb ends in -e, which is not pronounced, then the II and III forms of the verb are formed by adding the ending - d: to arrive (arrive) - arrived (arrived).
Irregular Verbs

Irregular Verbs- these are verbs that have special, fixed forms of the past tense and participles, their forms do not have a clear education algorithm and are learned by memorizing: to make (to do) - made (done) - made (done). Most English irregular verbs are native English, derived from verbs that existed in Old English. Most irregular verbs exist as remnants of historical systems of conjugation (changing the verb by person - I'm coming, you're coming, he's coming...).
Irregular verbs are used to form the past simple (Past Simple), present perfect (Present Simple), past perfect tense (Past Perfect), in the passive voice (Passive voice), when converting direct speech into indirect (Reported speech), in conditional sentences ( conditional sentences).
table of irregular verbs
| Infinitive | past tense | Past Participle | Translation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arise | [ə"raiz] | arose | [ə"rəuz] | arisen | [ə"riz(ə)n] | arise, appear |
| wake up | [ə"weik] | awoke | [ə"wəuk] | awoken | [ə"wəukən] | wake up, wake up |
| be | was, were | , | been | be | ||
| bear | bore | born | give birth, bring | |||
| beat | beat | beaten | ["bi:tn] | beat | ||
| become | became | become | become | |||
| begin | started | begun | start off) | |||
| bend | bent | bent | bend, bend | |||
| bind | bound | bound | bind | |||
| bite | bit | bitten | ["bɪtn] | bite) | ||
| bleed | bled | bled | bleed | |||
| blow | blew | blown | blow | |||
| break | broke | broken | ["broukən] | break) | ||
| breed | bred | bred | bring up | |||
| bring | brought | brought | bring | |||
| build | built | built | build | |||
| burn | burnt | burnt | burn, burn | |||
| burst | burst | burst | explode, explode | |||
| buy | bought | bought | buy | |||
| cast | cast | cast | throw, pour (metal) | |||
| catch | caught | caught | catch, seize | |||
| choose | chose | chosen | ["tʃouzən] | choose, pick | ||
| come | came | come | come | |||
| cost | cost | cost | cost | |||
| cut | cut | cut | cut | |||
| dig | arc | arc | dig, dig | |||
| do | did | done | do | |||
| draw | drew | drawn | draw, draw | |||
| dream | dream | dream | dream, dream | |||
| drink | drank | drunk | drink | |||
| drive | drove | driven | ["drɪvən] | drive | ||
| eat | ate | eaten | ["i:tn] | There is | ||
| fall | fell | fallen | ["fɔ:lən] | fall | ||
| feed | fed | fed | feed | |||
| feel | felt | felt | feel | |||
| fight | fought | fought | fight | |||
| find | found | found | find | |||
| fit | fit | fit | fit in size | |||
| fly | flew | flown | fly | |||
| forget | forgot | forgotten | forget | |||
| forgive | forgave | forgiven | forgive | |||
| freeze | frozen | frozen | ["frouzən] | freeze | ||
| get | got | got | receive | |||
| give | gave | given | ["gɪvən] | give | ||
| go | went | gone | go, walk | |||
| grow | grew | grown | grow | |||
| hang | hung | hung | hang, hang | |||
| have | had | had | have | |||
| hear | heard | heard | hear | |||
| hide | hidden | hidden | ["hɪdn] | hide | ||
| hit | hit | hit | hit the mark | |||
| hold | held | held | hold | |||
| hurt | hurt | hurt | hurt, bruise | |||
| keep | kept | kept | keep, save | |||
| kneel | knelt | knelt | kneel | |||
| knit | knit | knit | knit (knitting needles) | |||
| know | knew | known | know | |||
| lay | laid | laid | put | |||
| lead | led | led | lead, lead | |||
| lean | lean | lean | tilt | |||
| learn | learned | learned | learn | |||
| leave | left | left | leave, leave | |||
| lend | lent | lent | borrow, borrow | |||
| let | let | let | let | |||
| lie | lay | lain | lie | |||
| light | lit | lit | illuminate, ignite | |||
| lose | lost | lost | lose | |||
| make | made | made | do | |||
| mean | meant | meant | to mean | |||
| meet | met | met | meet | |||
| mistake | mistook | mistaken | make mistakes | |||
| pay | paid | paid | to pay | |||
| put | put | put | put, put | |||
| read | read | read | read | |||
| ride | rode | ridden | ["rɪdn] | ride | ||
| ring | rank | rung | call, call | |||
| rise | rose | rising | ["rɪzən] | get up | ||
| run | ran | run | run away | |||
| say | said | said | speak | |||
| see | saw | seen | see | |||
| seek | sought | sought | search | |||
| sell | sold | sold | sell | |||
| send | sent | sent | send | |||
| set | set | set | put, put | |||
| shake | [ʃeɪk] | shook | [ʃʊk] | shaken | ["ʃeɪkən] | shake |
| shine | [ʃaɪn] | shone | [ʃoun, ʃɒn] | shone | [ʃoun, ʃɒn] | to shine, shine, shine |
| shoot | [ʃu:t] | shot | [ʃɒt] | shot | [ʃɒt] | fire |
| show | [ʃou] | showed | [ʃoud] | shown | [ʃoun] | show |
| shrink | [ʃriŋk] | shrank | [ʃræŋk] | shrunk | [ʃrʌŋk] | sit down (about the material), decrease (sya), reduce (sya) |
| shut | [ʃʌt] | shut | [ʃʌt] | shut | [ʃʌt] | close |
| sing | sang | sung | sing | |||
| sink | sank | sunk | drown | |||
| sit | sat | sat | sit | |||
| sleep | slept | slept | sleep | |||
| smell | smelt | smelt | smell, smell | |||
| slide | slide | slide | slide | |||
| sow | sowed | sown | sow, sow | |||
| smell | smelled | smelled | smell, smell | |||
| speak | spoke | spoken | ["spoukən] | speak | ||
| spell | spelt | spelt | to spell | |||
| spend | spent | spent | spend | |||
| spill | spilt | spilt | shed | |||
| sleep | spat | spat | spit | |||
| split | split | split | split | |||
| spoil | spoilt | spoilt | spoil | |||
| spread | spread | spread | spread | |||
| stand | stood | stood | stand | |||
| steal | stole | stolen | ["stoulən] | steal | ||
| stick | stuck | stuck | to stick, to stick, to stick | |||
| sting | stung | stung | sting | |||
| strike | struck | struck | hit, strike | |||
| striving | strove | striving | ["strɪvn] | try, strive | ||
| wear | swore | sworn | take an oath | |||
| sweep | swept | swept | revenge, sweep | |||
| swim | swam | swum | swim | |||
| take | took | taken | ["teɪkən] | take, take | ||
| teach | taught | taught | learn | |||
| tear | tore | torn | tear | |||
| tell | told | told | tell | |||
| think | [θɪŋk] | thought | [θɔ:t] | thought | [θɔ:t] | think |
| throw | [θrou] | threw | [θru:] | thrown | [θroun] | throw |
| understand | [ʌndər "stænd] | understood | [ʌndər"stʊd] | understood | [ʌndər"stʊd] | understand |
| upset | [ʌp"set] | upset | [ʌp"set] | upset | [ʌp"set] | upset, upset (plans), upset |
| wake | woke | woken | ["woukən] | wake up | ||
| wear | wore | worn | wear | |||
| weep | wept | wept | cry | |||
| wet | wet | wet | wet, moisturize | |||
| win | won | won | win, win | |||
| wind | wound | wound | writhing, winding, winding (clock) | |||
| write | wrote | written | ["rɪtn] | write |
How to remember forms of irregular verbs?

Irregular Verbs in English, these are verbs that have special forms (Past Simple) and (Past Participle). Among them there are both very common (feel - to feel, speak - to speak), and rare (cleave - to dissect, forswear - to renounce). The tables below show common irregular verbs.
Read also:
Despite the fact that irregular verbs change in a special way, they still have some regularity. In the table below, the verbs are given with translation and transcription and are distributed on the basis of matching forms:
- Verbs AAA - all three forms are the same (cut - cut - cut, cut).
- Verbs ABA - the 1st and 3rd forms coincide (run - ran - run, run).
- ABB verbs - the 2nd and 3rd forms coincide (teach - taught - taught, teach).
- ABC verbs - all forms are different (know - knew - known, know).
Inside the table, words are distributed not alphabetically, but by frequency, i.e. the higher the word, the more often it is used. Attached to the tables pdf files- they can be printed, pasted on cardboard and cut out cards for memorizing words.
| Verbs like AAA: the same in three forms Download PDF | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Translation | Infinitive | past simple | Past Participle |
| put | put |
put |
put |
| let | let |
let |
let |
| cut | cut |
cut |
cut |
| put (install) | set |
set |
set |
| bet | bet |
bet |
bet |
| throw (cast metal) | cast |
cast |
cast |
| cost | cost |
cost |
cost |
| beat | hit |
hit |
hit |
| to cause a pain | hurt |
hurt |
hurt |
| to knit | knit |
knit |
knit |
| stop | quit |
quit |
quit |
| distribute | spread |
spread |
spread |
| ABA type verbs: forms 1 and 3 are the same | |||
| run away | run |
ran |
run |
| come | come |
came |
come |
| become | become |
became |
become |
| ABB type verbs: forms 2 and 3 are the same | |||
| read | read |
read |
read |
| to teach (learn) | learn |
learned (learned) |
learned (learned) |
| think | think [θiŋk] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
| to teach (teach) | teach |
taught |
taught |
| smell (smell) | smell |
smelt |
smelt |
| hear | hear |
heard |
heard |
| hold | hold |
held |
held |
| bring | bring |
brought |
brought |
| stand | stand |
stood |
stood |
| lose (lose) | lose |
lost |
lost |
| meet | meet |
met |
met |
| lead | lead |
led |
led |
| understand | understand [ʌndə'stænd] |
understood [ʌndə'stud] |
understood [ʌndə'stud] |
| win | win |
won |
won |
| buy | buy |
bought |
bought |
| send | send |
sent |
sent |
| sell | sell |
sold |
sold |
| catch | catch |
caught |
caught kɔ:t] |
| fight | fight |
fought |
fought |
| put (put) | lay |
laid |
laid |
| sit | sit |
sat |
sat |
| bind | bind |
bound |
bound |
| bleed | bleed |
bled |
bled |
| build | build |
built |
built |
| burn | burn |
burnt |
burnt |
| deal with | deal |
dealt |
dealt |
| dig | dig |
arc |
arc |
| feed | feed |
fed |
fed |
| hang | hang |
hung |
hung |
| hide | hide |
hidden |
hidden [‘hɪdn] |
| lean | lean |
lean (leaned) |
lean (leaned) |
| lend (to someone) | lend |
lent |
lent |
| illuminate | light |
lit |
lit |
| ride | ride |
rode |
ridden [‘rɪdn] |
| sew | sew |
sewed |
sewed (sewn) |
| write or spell | spell |
spelt |
spelt |
| shed | spill |
spilt |
spilt |
| spit | sleep |
spat (spit) |
spat (spit) |
| spoil | spoil |
spoilt |
spoilt |
| stick | stick |
stuck |
stuck |
| strike | strike |
struck |
struck |
| sweep | sweep |
swept |
swept |
| cry | weep |
wept |
wept |
| twist | wind |
wound |
wound |
| Type verbsABC: all shapes are different |
|||
| go | go |
went |
gone |
| know | know |
knew |
known |
| take | take |
took |
taken [‘teik(ə)n] |
| see | see |
saw |
seen |
| give | give |
gave |
given |
| write | write |
wrote |
written [‘ritn] |
| speak | speak |
spoke |
spoken [‘spouk(e)n] |
| drive a car | drive |
drove |
driven [‘driven] |
| break | break |
broke |
broken ['brouk(e)n] |
| wear clothes) | wear |
wore |
worn |
| There is | eat |
ate |
eaten [‘i:tn] |
| drink | drink |
drank |
drunk |
| draw (pull) | draw |
drew |
drawn |
| steal | steal |
stole |
stolen [‘stəulən] |
| throw | throw [θrəu] |
threw [θru:] |
thrown [θrəun] |
| blow | blow |
blew |
blown |
| fall | fall |
fell |
fallen [‘fɔ:lən] |
| start off | begin |
started |
begun |
| forget | forget |
forgot |
forgotten |
| forgive | forgive |
forgave |
forgiven |
| fly | fly |
flew |
flown |
| freeze (freeze) | freeze |
frozen |
frozen [‘frouzn] |
| grow | grow |
grew |
grown |
| call | ring |
rank |
rung |
| shake | shake [ʃeik] |
shook [ʃuk] |
shaken [‘ʃeik(ə)n] |
| sing | sing |
sang |
sung |
| stink | stink |
stank (stunk) |
stun |
| try | striving |
strove |
striving [‘strɪvn] |
| to swear | wear |
swore |
sworn |
| tear | tear |
tore |
torn |
| wake | wake |
woke |
woken [‘wouk(e)n] |
Pay attention to the words read And wind. In the 2nd and 3rd forms, read is read as . And the verb wind - to twist, should not be confused with the noun wind - wind.
The Ten Most Basic Irregular Verbs
Among the commonly used irregular verbs, one can distinguish the most basic. They need to be known first. Start learning verbs from them, not in alphabetical order. You can learn them literally in 5-10 minutes.
| Translation | Infinitive (1st form) | Past Simple (2nd form) | Past Participle (3rd form) |
|---|---|---|---|
| go | go |
went |
gone |
| know | know |
knew |
known |
| think | think [θiŋk] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
thought [θɔ:t] |
| take | take |
took |
taken [‘teik(ə)n] |
| see | see |
saw |
seen |
| give | give |
gave |
given |
| write | write |
wrote |
written [‘ritn] |
| speak | speak |
spoke |
spoken [‘spouk(e)n] |
| hear | hear |
heard |
heard |
| buy | buy |
bought |
bought |
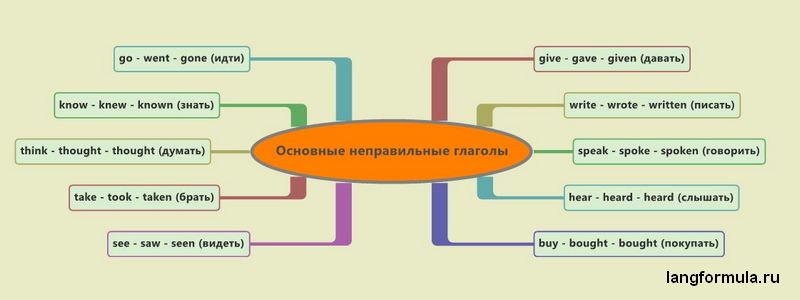
These verbs need to be learned first
Notes:
- Over time, some verbs from irregular have almost turned into regular ones. For example, even in not very old textbooks it is written that the verb to work- incorrect, it has the form: work - wrought - wrought. Now form wrought almost never used, except in established expressions like "wrought iron" (forged iron), so I did not include it in this table.
- Verbs to learn(learn), to lean(lean) are also more often used as correct ones: learned, leaned, especially in the USA.
- Pay attention to forms read-read-read. The word is spelled the same but pronounced differently.
- Don't confuse the verb wind(twist) and noun wind- wind. They are spelled the same but have different pronunciations and meanings.
- In the British version, the verbs sew pronounced like
Our topic today is an acquaintance with such an interesting phenomenon as the forms of irregular verbs. As you know, the English language is very cunning. This language often lays all sorts of traps for us. One of them is irregular verbs. English is not the only language that has irregular verbs. French is also rich in irregular verbs.
Three or four forms of irregular English verbs?Romanian, German, Latin, Greek also contain irregular verbs. And even the Russian language is replete with them. I think you have repeatedly heard about irregular verbs in English, in other words, Irregular Verbs. Why are such verbs called irregular? Everything is very simple: in the past tense they are conjugated in their own way, have their own special form, while all other verbs in the past tense have the ending -ed.
For comparison, let's conjugate 3 regular regular verbs in the simple past tense (Past Simple):
| work- ra | sing | |
| I worked | I translated | I managed |
| You worked | you translated | You managed |
| He worked | He translated | He managed |
| She worked | She translated | She managed |
| It worked | It translated | It managed |
| We worked | We translated | We managed |
| They worked | they translated | They managed |
As you can see, all 3 verbs are conjugated in the same way, according to the scheme stem + ending -ed.
The situation is quite different in the case of irregular verbs. We conjugate 3 more verbs in the simple past tense (Past Simple), which are incorrect, and here pay attention to the fact that each of these verbs has its own, completely different form at the end or even at the root of the word:
| blow- blow | go- go | bring- bring |
| I blew | I went | I brought |
| You blew | You went | You brought |
| He blew | He went | He brought |
| She blew | She went | She brought |
| It blew | It went | It brought |
| We blew | We went | We brought |
| They blew | They went | They brought |
Even to the naked eye it is clear that each of these verbs appeared in its own, completely different from the others, form. The catch is that there is no specific rule by which you can find out the form of an irregular verb. Each of them hides in their own way. The English language, friends, is full of tricky things and underwater reefs. Another catch is that each irregular verb has not one form, but three.
Three forms of irregular verbs
So what are these three forms?
- The first is the infinitive or initial (indefinite) form of the verb
- The second is Past Participle I, that is, the form that corresponds to the simple past tense (Past Simple), it is also used in the 2nd and 3rd cases of the conditional mood (Conditional of the 2-d and of the 3-d case)
- The third is Past Participle II, the one that is used in the perfect present tense (Present Perfect) and in the past tense (Past Perfect). The same form is used in the Passive Voice, Conditional of the 3-d case, and some other grammatical rules.
Here are some examples of 3 forms of irregular verbs:
- To arise - arose - arisen - rise
- To be - was, were - been - to be
- To bear - bore - born - give birth
- To become - became - become - become, become
- To begin - began - begun - begin
- To catch - caught - caught - catch, catch
- To choose - chose - chosen - choose
- To dig - dug - dug - dig, dig
- To dream - dream - dream - dream, dream
- To feel - felt - felt - feel
- To forget - forgot - forgotten - forget
- To have - had - had - to have
Now let's look at these 3 forms using examples of sentences in all of the above tenses of verbs.
- So, the simple past tense of the verb (Past Simple Tense):
Yesterday she felt(self-bad) to feel). She felt bad yesterday. Last Wednesday we met Jim ( to meet). We met Jim last Wednesday. Last night I dream you ( to dream). “I dreamed about you last night. I was in Paris last year ( to be) — I was in Paris last year.
- Perfect present tense of the verb (Present Perfect Tense):
I have just seen him ( to see). “I just saw him. Tom has already brought my books ( to bring). Tom has already brought my books. Have you ever been in London to be)? - Have you ever been in London? Ann has already forgotten her boy-friend( to forget).- Anna has already forgotten her boyfriend.
- The past tense of the verb (Past Perfect Tense):
I noticed that I had forgotten my keys( to forget). — I noticed that I forgot my keys. He understood that he had lost his documents ( to lose). He realized that he had lost his papers.
- Passive voice (Passive Voice):
The dog is fed by me ( to feed). The dog is fed by me (I fed the dog). Made in France ( to make). - Made in France.
- Conditional mood of the 2nd and 3rd cases (Conditional). Here are the second and third forms:
If I had money, I would buy a car to have). - If I had money, I would buy a car (real condition). If I had money, I would have bought a car ( to have, to buy).- If I had money, I would buy a car (unreal condition, past tense).
 How to learn all forms of irregular verbs?
How to learn all forms of irregular verbs? Irregular Verbs Cheat Sheet
As mentioned above, there are no rules by which the forms of irregular verbs are formed, each has its own. But, we hope that this poetic form will help you quickly remember such irregular verbs:
To write-wrote-written
To eat-ate-eat
To speak-spoke-spoken
To break-broke-broken
To come-came-come
To become-became-become
To run-run-run
To swim swam swum
To know-knew-known
To throw-threw-thrown
To blow-blew-blown
To fly-flew-flown
Tossing-sang-sung
To ring-rang-rung
To hide-hid-hidden
To bite-bit-bitten
To send-sent-sent
To spend-spent-spent
To sleep-slept-slept
To keep-kept-kept
To tell-told-told
To sell-sold-sold
To teach-taught-taught
To catch-caught-caught
To fight-fought-fought
To think-thought-thought
To buy-bought-bought
To bring-brought-brought
To cut-cut-cut
To shut-shut-shut
To cost-cost-cost
To lose-lost-lost
To lead-led-led
To feed-fed-fed
To feel-felt-felt
To hold-held-held
From this funny poetic form, we see that some irregular verbs have the same letter combinations, which allows them to rhyme and thus make it easier for us to memorize them.
The "fourth" form of irregular verbs
There is a popular belief that there is also a 4th form of irregular verbs. This 4th configuration is formed according to the scheme base + ending -ing. It defines the Present Participle, that is, the present participle in tenses such as the present continuous (Present Continuous) and the past continuous (Past Continuous). In other words, this is the present and past tense of the imperfect form. It follows from this that there are not 3, but 4 forms of irregular verbs. But this 4th configuration is, as it were, unofficial.
I'll tell you a secret: regular and irregular verbs of the English language are the most "favorite" topic for teachers and students when studying English grammar. Fate wanted the most popular and frequently used words in English speech to be incorrect. For example, the famous phrase "to be or not to be" also contains exactly the wrong verb. And that's the beauty of the British :)
Just think for a second how great it would be to add an ending -ed to the main verbs and get the past tense. And now all English learners are prepared to participate in an exciting attraction - memorizing a convenient table of irregular English verbs with translation and transcription.
1. IRREGULAR VERBS
Meet their royal majesty irregular verbs. It won't take long to talk about them. You just need to accept and remember that each verb has its own forms. And it is almost impossible to find any logical connection. It remains only to put a table in front of you and learn how you once memorized the English alphabet.
It's good that there are verbs where all three forms coincide and are pronounced the same (put-put-put). But there are especially harmful forms that are written like twins, but are pronounced differently. (read - read - read ). Just like choosing only the best tea leaves of the best varieties for the royal tea party, we have collected the most used irregular verbs, arranged them alphabetically, visually conveniently arranged in a table - we did everything to make you smile and ... learn. In general, only conscientious cramming will save humanity from ignorance of English irregular verbs.
And to make memorization not so boring, you can create your own algorithms. For example, first write out all the verbs where the three forms match. Then those where the two forms coincide (most of them, by the way). Or, let's say, learn words today with the letter "b" (do not think bad), and tomorrow - with another. No limits to fantasy for lovers of English!
And without departing from the cash register, we suggest taking a test for knowledge of irregular verbs.
Table of irregular verbs in English with transcription and translation:
| indefinite form of the verb (Infinitive) | simple past tense (Past Simple) | past participle | Translation | |
| 1 | abide [ə"baɪd] | abode [ə"bəud] | abode [ə"bəud] | stay, stick to something |
| 2 | arise [ə"raɪz] | arose [ə"rəuz] | arisen [ə "rɪz (ə) n] | arise, rise |
| 3 | awake [ə"weɪk] | awoke [ə"wəuk] | awoken [əˈwoʊkn] | wake up, wake up |
| 4 | be | was; were | been | to be, to be |
| 5 | bear | bore | born | wear, give birth |
| 6 | beat | beat | beaten ["bi:tn] | beat |
| 7 | become | became | become | become, become |
| 8 | fall | befell | befallen | happen |
| 9 | begin | started | begun | start off) |
| 10 | hold | beheld | beheld | look, notice |
| 11 | bend | bent | bent | bend(s), bend(s) |
| 12 | beseech | thought | thought | beg, beg |
| 13 | beset | beset | beset | surround, besiege |
| 14 | bet | bet | bet | bet |
| 15 | bid | bid | bid | bid, order, ask |
| 16 | bind | bound | bound | bind |
| 17 | bite | bit | bitten ["bɪtn] | bite) |
| 18 | bleed | bled | bled | bleed, bleed |
| 19 | blow | blew | blown | blow |
| 20 | break | broke | broken ["brəuk(ə)n] | break, break, break |
| 21 | breed | bred | bred | breed, breed, breed |
| 22 | bring | brought | brought | bring, bring |
| 23 | broadcast ["brɔːdkɑːst] | broadcast ["brɔːdkɑːst] | broadcast ["brɔːdkɑːst] | broadcast, distribute |
| 24 | build | built | built | build, build |
| 25 | burn | burnt | burnt | burn, burn |
| 26 | burst | burst | burst | explode) |
| 27 | buy | bought | bought | buy |
| 28 | can | could | could | be able to physically |
| 29 | cast | cast | cast | throw, pour (metal) |
| 30 | catch | caught | caught | catch, seize |
| 31 | choose [ʧuːz] | chose [ʧuːz] | chosen ["ʧəuz(ə)n] | choose |
| 32 | cling | clung | clung | stick, cling, cling |
| 33 | cleave | cleft | cloven ["kləuv(ə)n] | cut, split |
| 34 | clothes | clothed | clothed | dress, dress |
| 35 | come | came | come [ kʌm] | come |
| 36 | cost | cost[ kɒst] | cost[ kɒst] | evaluate, cost |
| 37 | creep | crept | crept | crawl |
| 38 | cut | cut [ kʌt] | cut [ kʌt] | cut, trim |
| 39 | dare | Durst | dared | dare |
| 40 | deal | dealt | dealt | to deal, to trade, to deal |
| 41 | dig | arc | arc | dig |
| 42 | dive | dove | dived | dive |
| 43 | do/does | did | done | do |
| 44 | draw | drew | drawn | drag, draw |
| 45 | dream | dream | dream | dream, dream |
| 46 | drink | drank | drunk | drink, drink |
| 47 | drive | drove | driven [ˈdrɪvn̩] | drive, drive, drive, drive |
| 48 | dwell | dwelt | dwelt | dwell, abide, linger on something |
| 49 | eat | ate | eaten [ˈiːtn̩] | eat, eat, eat |
| 50 | fall | fell | fallen [ˈfɔːlən] | fall |
| 51 | feed | fed | fed[ fed] | feed) |
| 52 | feel | felt | felt [ felt] | feel |
| 53 | fight | fought [ˈfɔːt] | fought [ˈfɔːt] | fight, fight |
| 54 | find | found | found | find |
| 55 | fit | fit[ fɪt] | fit[ fɪt] | fit, fit |
| 56 | fleece | fled | fled | run away, flee |
| 57 | fling | flung | flung | throw, throw |
| 58 | fly | flew | flown | fly, fly |
| 59 | forbid | forbade | forbidden | forbid |
| 60 | forecast [ˈfɔːkɑːst] | forecast; forecasted [ˈfɔːkɑːstɪd] | foresee, predict | |
| 61 | forget | forgot | forgotten | forget |
| 62 | forego | future | foregone | refuse, refrain |
| 63 | foretell | foretold | foretold | predict, forecast |
| 64 | forgive | forgave | forgiven | forgive, |
| 65 | forsake | forsook | forsaken | throw, refuse |
| 66 | freeze | frozen | frozen [ˈfrəʊzən] | freeze, freeze |
| 67 | get [ˈɡet] | got [ˈɡɒt] | got [ˈɡɒt] | get, become |
| 68 | gild [ɡɪld] | gilt [ɡɪlt]; gilded [ˈɡɪldɪd] | gild | |
| 69 | give [ɡɪv] | gave [ɡeɪv] | given [ɡɪvn̩] | give |
| 70 | go/goes [ɡəʊz] | went [ˈwent] | gone [ɡɒn] | go, go |
| 71 | grind [ɡraɪnd] | ground [ɡraʊnd] | ground [ɡraʊnd] | sharpen, grind |
| 72 | grow [ɡrəʊ] | grew [ɡruː] | grown [ɡrəʊn] | grow, grow |
| 73 | hang | hung; hanged | hang [ hʌŋ]; hanged [ hæŋd] | hang, hang |
| 74 | have | had | had | to have, to possess |
| 75 | hew | hewed | hewed; hewn | to cut, to cut |
| 76 | hear | heard | heard | hear |
| 77 | hide | hidden | hidden [ˈhɪdn̩] | hide, hide |
| 78 | hit | hit[ hɪt] | hit[ hɪt] | hit, hit |
| 79 | hold | held | held | hold, maintain (possess) |
| 80 | hurt | hurt | hurt | hurt, hurt, injure |
| 81 | keep | kept | kept | keep, store |
| 82 | kneel | knelt; kneeled | kneel | |
| 83 | knit | knit ; knitted [ˈnɪtɪd] | to knit | |
| 84 | know | knew | known | know |
| 85 | lay | laid | laid | put |
| 86 | lead | led | led | lead, accompany |
| 87 | lean | leant; leaned | lean on, lean on | |
| 88 | leap | leapt; leaped [lipt] | leapt; leaped | jump |
| 89 | learn | learned; learned | to learn, to know | |
| 90 | leave | left | left | leave, leave |
| 91 | lend | lent | lent[lent] | lend, lend |
| 92 | let | let[let] | let[let] | let, let |
| 93 | lie | lay | lain | lie |
| 94 | light | lit ; lighted [ˈlaɪtɪd] | lit [lɪt]; lighted [ˈlaɪtɪd] | kindle, illuminate |
| 95 | lose | lost | lost | lose |
| 96 | make [ˈmeɪk] | made [ˈmeɪd] | made [ˈmeɪd] | do, force |
| 97 | may | might | might | be able to have the right |
| 98 | mean | meant | meant | mean, imply |
| 99 | meet | met | met | meet, meet |
| 100 | mishear [ˌmɪsˈhɪə] | misheard [ˌmɪsˈhɪə] | misheard [ˌmɪsˈhɪə] | misheard |
| 101 | mislay | mislaid | mislaid | misplace |
| 102 | mistake | mistook | mistaken | to err, to be mistaken |
| 103 | mow | moved | mown | mow |
| 104 | overtake | overcurrent | overtaken | catch up |
| 105 | pay | paid | paid | to pay |
| 106 | prove | proved | proven; proven | prove, certify |
| 107 | put | put | put | put |
| 108 | quit | stop; quitted | stop; quitted | leave, leave |
| 109 | read | read; red | read; red | read |
| 110 | rebuild | rebuilt | rebuilt | rebuild, restore |
| 111 | rid | rid; ridded | rid; ridded | free, deliver |
| 112 | ride | rode | ridden | ride |
| 113 | ring | rank | rung | call, call |
| 114 | rise | rose | rising | rise, ascend |
| 115 | run | ran | run | run, flow |
| 116 | saw | sawed | sawn; sawed | to nag |
| 117 | say | said | said | speak, say |
| 118 | see | saw | seen | see |
| 119 | seek | sought | sought | search |
| 120 | sell | sold | sold | sell |
| 121 | send | sent | sent | send, send |
| 122 | set | set | set | place, put |
| 123 | sew | sewed | sewed; sewn | sew |
| 124 | shake | shook | shaken | shake |
| 125 | shall | should | should | be to |
| 126 | shave | shaved | shaved | to shave) |
| 127 | shear | sheared | shorn | cut, cut; deprive |
| 128 | Shed | Shed | Shed | throw off, spill |
| 129 | shine | shone; shined | shone; shined | shine, shine |
| 130 | shoes | shod | shod | shoe, shoe |
| 131 | shoot | shot | shot | fire |
| 132 | show | showed | shown; showed | show |
| 133 | shrink | shrank; shrunk | shrunk | shrink, shrink, rebound, recoil |
| 134 | shut | shut | shut | close |
| 135 | sing | sang | sung | sing |
| 136 | sink | sank | sunk | sink, sink, sink |
| 137 | sit | sat | sat | sit |
| 138 | slay | slew | slain | kill, destroy |
| 139 | sleep | slept | slept | sleep |
| 140 | slide | slide | slide | slide |
| 141 | sling | slung | slung | throw, throw, hang over the shoulder, hang |
| 142 | slit | slit | slit | cut lengthwise |
| 143 | smell | smelt; smelled | smelt; smelled | smell, sniff |
| 144 | sow | sowed | sowed; sown | sow |
| 145 | speak | spoke | spoken | speak |
| 146 | speed | sped; speeded | sped; speeded | hurry, speed up |
| 147 | spell | spell; spelled | spell; spelled | write, spell a word |
| 148 | spend | spent | spent | spend, waste |
| 149 | spill | spilt | spilt | shed |
| 150 | spin | spun | spun | spin |
| 151 | sleep | spat | spat | spit, stick, poke, pro- |
| 152 | split | split | split | split, split |
| 153 | spoil | spoilt; spoiled | spoilt; spoiled | spoil, spoil |
| 154 | spread | spread | spread | spread |
| 155 | spring | sprang | sprung | jump, jump |
| 156 | stand | stood | stood | stand |
| 157 | steal | stole | stolen | steal, steal |
| 158 | stick | stuck | stuck | to stick, to stick, to stick |
| 159 | sting | stung | stung | sting |
| 160 | stink | stank; stun | stun | stink, repel |
| 161 | strew | strewed | strewn; strewed | to scatter, scatter, spread |
| 162 | stride | strode | stridden | step |
| 163 | strike | struck | struck | hit, hit, strike |
| 164 | string | string | string | bind, tie, string |
| 165 | striving | strove | striving | strive, try |
| 166 | wear | swore | sworn | swear, swear, scold |
| 167 | sweep | swept | swept | to sweep |
| 168 | swell | swollen | swollen; swollen | to swell, swell, swell |
| 169 | swim | swam | swum | swim |
| 170 | swing | swung | swung | swing, swing |
| 171 | take | took | taken | take |
| 172 | teach | taught | taught | teach, teach |
| 173 | tear | tore | torn | tear, times-, with-, from- |
| 174 | tell | told | told | to tell, inform |
| 175 | think | thought | thought | think |
| 176 | throw | threw | thrown | throw, throw |
| 177 | thrust | thrust | thrust | push, poke, kick out, shove |
| 178 | thread | trod | trod; trodden | step |
| 179 | unbend | unbent | unbent | unbend |
| 180 | undergo | life | undergone | experience, endure |
| 181 | understand | understood | understood | understand |
| 182 | undertake | undertook | glimpsed | undertake, guarantee |
| 183 | upset | upset | upset | overturn, squeeze |
| 184 | wake | woke; waked | woke; waked | wake up, wake up |
| 185 | wear | wore | worn | wear clothes) |
| 186 | weave | wove; weaved | woven; weaved | weave |
| 187 | wed | wed; married | wed; married | to get married, to get married |
| 188 | weep | wept | wept | cry |
| 189 | will | would | would | want to be |
| 190 | wet | wet; wetted | wet; wetted | wet, you-, pro- |
| 191 | win | won | won | win, get |
| 192 | wind | wound | wound | wind up (mechanism), curl |
| 193 | withdraw | withdrew | withdrawn | take back, take away |
| 194 | ring | wrung | wrung | squeeze, squeeze, twist |
| 195 | write | wrote | written | write |
After this video, you will love learning irregular verbs! Yo! :) ...it is advisable for the impatient to watch from 38 seconds
For fans of an advanced teacher and rap lovers, we offer a backing track for a personal way of learning irregular verbs in the karaoke style, and in the future, perhaps, for recording a new personal video with your teacher / teacher / class. Weak or not weak?
2. REGULAR VERBS
When the most difficult part in the form of irregular verbs is mastered (we want to believe that this is so), you can click like nuts and regular English verbs. They are called so because they form the past tense and participle II in exactly the same way. In order not to load your brain once again, we simply denote their form 2 and form 3. And both of them are obtained with the help of the ending - ed.
For example: look-look,work - worked
2.1 And for those who like to get to the bottom of everything in everything, you can conduct a brief educational program about the mysterious term " participle II". First, why participle? Because how else to designate a three-headed dragon, which has signs of 3 parts of speech at once: a verb, an adjective and an adverb. Accordingly, such a form is always found WITH PARTS (at once with three).
Second, why II? Because there is also I . Quite logical Only participle I has an ending -ing, and participle II has an ending -ed in regular verbs, and any ending in irregular ones ( written , built , come ).
2.2 And everything would be fine, but there are some nuances.
If the verb ends with -y, then you need an ending -ied(study-study).
. If the verb consists of one syllable and ends in a consonant, then it doubles ( stop - stopped).
. The final consonant l is always doubled (travel -travelled)
. If the verb ends in -e, then you only need to add -d(translate - translated)
For especially corrosive and attentive, you can also add pronunciation features. For example, after deaf consonants, the ending is pronounced as “t”, after voiced - “d”, after vowels “id”.
Perhaps you heard / invented / read / spied on a way to minimize effort and maximize the efficiency of memorizing irregular verbs, but for some reason we don’t know it yet. Share not only your smile, but also cramming options to please each other with something interesting
English is the language of exceptions, where when studying a new grammatical rule, students are faced with a dozen buts in which this rule does not work. One of these rules is the use of irregular verbs in the past tense. For many English learners, this topic is a nightmare. But without them it is impossible, because these are the realities of English! However, there is good news - modern English is gradually getting rid of irregular verbs, replacing them with regular ones. Why and how - we will consider in the article.
Why are English verbs irregular?
The difficulty in using irregular verbs is experienced not only by foreigners, but also by the speakers themselves. Nevertheless, for English philologists, the non-standard nature of this part of speech is not a drawback, but a reason for pride. They believe that irregular verbs are a cultural monument that perpetuates the history of the English language. The explanation for this fact is the Germanic roots of the origin of irregular verbs, which makes British English a traditional variant of the language. For comparison, the Americans are trying with might and main to get rid of the wrong form, converting it into the correct one. Therefore, the list of non-standard verbs increases for those who learn both variants of the language. Thus, the incorrect version is ancient, which is reflected in prose and poetry.
How many forms does a verb have in English?
Speaking about verbs in English, it should be noted that they have 3 forms:
- infinitive, aka ;
- I, or Participle I, - this form is used in the simple past tense (Past Simple) and the 2nd and 3rd cases of the conditional mood (Conditional of the 2-d and of the 3-d case);
- Past Participle II, or Participle II, for Past Perfect, Passive Voice and Conditional of the 3-d case.

The table "Three in English" is presented later in the article.
What are regular and irregular verbs? Education rules
Regular verbs are those in which the past form (Past Simple) and the form Participle II (Participle II) are formed by adding the ending -ed to the initial form. The table "Three forms of the verb in English. Regular verbs" will help you better understand this rule.
When forming the forms Participle I and Participle II, there are some features:
- if the verb ends with the letter -e, then adding -ed does not double it;
- the consonant in monosyllabic verbs is duplicated when added. Example: stop - stopped (stop - stopped);
- if the verb ends in -y followed by a consonant, then y is changed to i before adding -ed.
Irregular verbs are those that do not obey the general rule when forming temporary forms. In English, these include the simple past tense verb forms (Past Simple) and Participle II (Participle II).
Irregular verbs are formed with:
ablaut, in which the root is changed. Example: swim - swam - swum (swim - swam - swam);
the use of suffixes that are different from those accepted in the grammar of the language. Example: do - did - done (do - did - did);
the same or unchanged form. Example: cut - cut - cut (cut - cut - cut).
Due to the fact that each irregular verb has its own form of change, they should be learned by heart.
In total, there are 218 irregular verbs in English, of which approximately 195 are in active use.
Recent studies in the field of language show that rare verbs are gradually disappearing from the language due to the replacement of the 2nd and 3rd forms with regular verb forms, that is, the addition of the ending - ed. This fact is confirmed by the table "Three forms of the verb in English" - the table represents a number of verbs that have both regular and irregular forms.
table of irregular verbs
The table "Three forms of irregular verbs in English" includes the most frequently used verbs. The table shows 3 forms and a translation.

Irregular verbs came into modern English from Old English, which was spoken by the Angles and Saxons - British tribes.

Irregular verbs originated from the so-called strong verbs, each of which had its own type of conjugation.

Harvard researchers found that most of the verbs used are irregular, and they will remain so, as they are used more often than others.

In the history of the English language there is such a phenomenon when the correct verb became irregular. For example, sneak, which has 2 forms - sneaked and snuck.

Not only English learners have problems with verbs, but also native speakers, as even they get into awkward situations when it comes to this difficult part of speech.

One of them is Jennifer Garner, who has been sure all her life that the verb sneak is correct.

She was corrected by the host of one of the programs in which the actress took part. Dictionary in hand, he pointed out to Jennifer her mistake.

Therefore, do not be upset if you make mistakes when using irregular verbs. The main thing is that they do not become systematic.

Regular verbs
The table "Three forms of regular verbs in English with transcription and translation" is compiled on the basis of the most commonly used verbs.
Past Participle I and II |
|||
ask | |||
answer | |||
allow | |||
agree | |||
borrow, borrow | |||
copy, rewrite | |||
prepare | |||
close | |||
carry, drag | |||
call, call | |||
discuss | |||
decide, decide | |||
explain | explain | ||
slide | |||
cry, scream | |||
finish, finish, end | |||
shine | |||
rub | |||
grab | |||
to help | |||
happen, happen | |||
manage | |||
look | |||
like | |||
move, move | |||
manage | |||
be necessary, need | |||
open | |||
recall | |||
suggest | sajgest | ||
study, learn | |||
stop, stop | |||
start off | |||
travel | |||
speak | |||
transfer | transitlate | ||
try, try | |||
use | |||
worry | |||
walk, walk | |||
look | |||
work |
Examples of the use of 3 forms of verbs with translation
Above we looked at 3 forms of verbs in English. A table with examples of usage and translation will help reinforce the topic.

Here, for each grammatical construction, two examples are given - one with regular, the other with irregular verbs.
Grammar design | Example in English | Translation |
| past simple |
|
|
| Present perfect tense |
|
|
| Past Perfect Tense |
|
|
| Passive Voice |
|
|
| Conditional |
|
|
Exercises

For better memorization of irregular verbs, you need not only to learn them by heart and repeat, but also to perform various exercises.
Exercise 1. Before you is a table "Three forms of the verb in English. Irregular verbs." Fill in one of the three missing forms.
Exercise 2. Before you is a table "Three forms of the verb in English. Regular verbs." Insert forms Participle I and II.
Exercise 3. Using the tables, translate the following sentences into English.
- I was reading a book.
- We saw them yesterday.
- The Smiths lived in London until 2000. Then they moved to Manchester.
- Alice was a university student in 2014.
- They worked for the same company two years ago.
- He just finished training.
- When we were children, my mother often took us to this park.
- I drove a toy car as a child.

Answers to the exercises
Exercise 1.
Exercise 2.
asked, borrowed, closed, decided, explained, helped, started, travelled, used, worked.
Exercise 3
- I read a book.
- We saw them yesterday.
- The Smiths lived in London till 2000. Then they moved to Manchester.
- Alice was a student of Univercity in 2014.
- They worked in the same company two years ago.
- He has just finished training.
- When we were children we were taken for a walk to this park.
- I drove a toy car in my childhood.
Get in the habit of periodically repeating the basic forms of the English verb. A table with irregular verbs, exercises and periodic repetition will help you quickly cope with the difficulties of the English language.
